Patients suffering with hard-to-treat depression may get relief from noninvasive magnetic brain stimulation
Published in Health & Fitness
Not only is depression a debilitating disease, but it is also widespread. Approximately 20 million adult Americans experience at least one episode of depression per year.
Millions of them take medication to treat their depression. But for many, the medications don’t work: Either they have minimal or no effect, or the side effects are intolerable. These patients have what is called treatment-resistant depression.
One promising treatment for such patients is a type of brain stimulation therapy called transcranial magnetic stimulation.
This treatment is not new; it has been around since 1995. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration cleared transcranial magnetic stimulation in 2008 for adults with “non-psychotic treatment-resistant depression,” which is typically defined as a failure to respond to two or more antidepressant medications. More recently, in 2018, the FDA cleared it for some patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder and smoking cessation.
Insurance generally covers these treatments. Both the psychiatrist and the equipment operator must be certified. While the treatment has been available for years, the equipment to perform the procedure remains expensive enough that few private psychiatry practices can afford it. But with the growing recognition of the potential of transcranial magnetic stimulation, the price will likely eventually come down and access will be greatly expanded.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation is a noninvasive, pain-free procedure that has minimal to no side effects, and it often works. Research shows that 58% of once treatment-resistant patients experience a significant reduction in depression following four to six rounds of the therapy. More than 40 independent clinical trials – with more than 2,000 patients worldwide – have demonstrated that repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is an effective therapy for the treatment of resistant major depression.
As a professor and psychiatrist who has used transcranial magnetic stimulation to treat some of my patients, I have seen depression symptoms decrease even within the first two weeks of treatment. What’s more, the effects continue after the treatment has ended, typically for six months to a year. After that, the patient has the option of maintenance treatment.
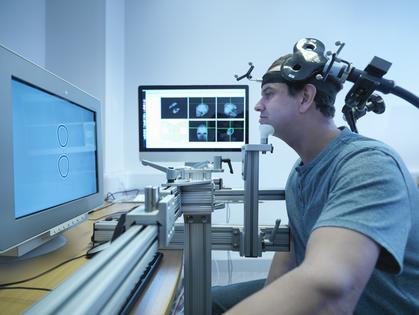
For the patient, the procedure is easy and simple. One sits in a comfortable chair with a snug pillow that holds their head in place, puts on earplugs and can then relax, check their phone, watch TV or read a book.
A treatment coil, which looks like a figure 8, is placed on the patient’s head. A nearby stimulator sends an electrical current to the coil, which transforms the current into a magnetic field.
The field, which is highly concentrated, turns on and off rapidly while targeting a portion of the prefrontal cortex – the area of the brain responsible for mood regulation.
...continued







Comments