Trump administration slashes number of diseases US children will be regularly vaccinated against
Published in News & Features
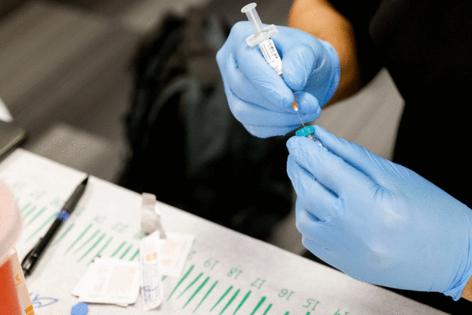
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services announced sweeping changes to the pediatric vaccine schedule on Monday, sharply cutting the number of diseases U.S. children will be regularly immunized against.
Under the new guidelines, the U.S. still recommends that all children be vaccinated against measles, mumps, rubella, polio, pertussis, tetanus, diphtheria, Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib), pneumococcal disease, human papillomavirus (HPV) and varicella, better known as chickenpox.
Vaccines for all other diseases will now fall into one of two categories: recommended only for specific high-risk groups, or available through “shared clinical decision-making” — the administration’s preferred term for “optional.”
These include immunizations for hepatitis A and B, rotavirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), bacterial meningitis, influenza and COVID-19. All these shots were previously recommended for all children.
Insurance companies will still be required to fully cover all childhood vaccines on the CDC schedule, including those now designated as optional, according to the Department of Health and Human Services.
The move has been anticipated since December, when President Donald Trump signed a presidential memorandum directing the health department and the CDC to update the pediatric vaccine schedule “to align with such scientific evidence and best practices from peer, developed countries.”
The new U.S. vaccinations guidelines are much closer to those of Denmark, which routinely vaccinates its children against only 10 diseases.
As pediatricians and public health experts have pointed out, Denmark also has a robust system of government-funded universal healthcare, a smaller and more homogenous population, and a different disease burden.
“The vaccines that are recommended in any particular country reflect the diseases that are prevalent in that country,” said Dr. Kelly Gebo, dean of the Milken Institute School of Public Health at George Washington University. “Just because one country has a vaccine schedule that is perfectly reasonable for that country, it may not be at all reasonable” elsewhere.
Almost every pregnant woman in Denmark is screened for hepatitis B, for example. In the U.S., less than 85% of pregnant women are screened for the disease.
Instead, the U.S. has relied on universal vaccination to protect children whose mothers don’t receive adequate care during pregnancy. Hepatitis B has been nearly eliminated in the U.S. since the vaccine was introduced in 1991.
“Viruses and bacteria that were under control are being set free on our most vulnerable,” said Dr. James Alwine, a virologist and member of the nonprofit advocacy group Defend Public Health. “It may take one or two years for the tragic consequences to become clear, but this is like asking farmers in North Dakota to grow pineapples. It won’t work and can’t end well.”
_____
©2026 Los Angeles Times. Visit at latimes.com. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.





Comments