The future of flight in a net-zero-carbon world: 9 scenarios, lots of sustainable biofuel
Published in Science & Technology News
Several major airlines have pledged to reach net-zero carbon emissions by midcentury to fight climate change. It’s an ambitious goal that will require an enormous ramp-up in sustainable aviation fuels, but that alone won’t be enough, our latest research shows.
The idea of jetliners running solely on fuel made from used cooking oil from restaurants or corn stalks might seem futuristic, but it’s not that far away.
Several airlines are already experimenting with sustainable aviation fuels. These include biofuels made from agriculture residues, trees, corn and used cooking oil. Other fuels are synthetic, made by combining captured carbon from the air and green hydrogen, made with renewable energy. Often, they can go straight into existing aircraft fuel tanks that normally hold fossil jet fuel.
United Airlines, which has been using a blend of used oil or waste fat and fossil fuels on some flights from Los Angeles and Amsterdam, announced in February 2023 that it had formed a partnership with biofuel companies to power 50,000 flights a year between its Chicago and Denver hubs using ethanol-based sustainable aviation fuels by 2028.
In a new study, we examined different options for aviation to reach net-zero emissions and assessed how air travel could continue without contributing to climate change.
The bottom line: Each pathway has important trade-offs and hurdles. Replacing fossil jet fuel with sustainable aviation fuels will be crucial, but the industry will still need to invest in direct-air carbon capture and storage to offset emissions that can’t be cut.
Before the pandemic, in 2019, aviation accounted for about 3.1% of total global CO₂ emissions from fossil fuel combustion, and the number of passenger miles traveled each year was rising. If aviation emissions were a country, that would make it the sixth-largest emitter, closely following Japan.
In addition to releasing carbon emissions, burning jet fuel produces soot and water vapor, known as contrails, that contribute to warming, and these are not avoided by switching to sustainable aviation fuels.
Aviation is also one of the hardest-to-decarbonize sectors of the economy. Small electric and hydrogen-powered planes are being developed, but long-haul flights with lots of passengers are likely decades away.
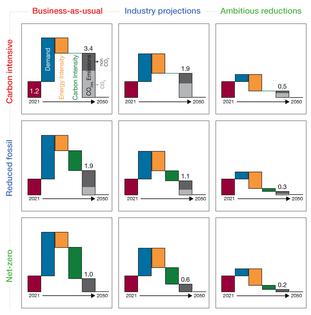
We developed and analyzed nine scenarios spanning a range of projected passenger and freight demand, energy intensity and carbon intensity of aviation to explore how the industry might get to net-zero emissions by 2050.
We found that as much as 19.8 exajoules of sustainable aviation fuels could be needed for the entire sector to reach net-zero CO₂ emissions. With other efficiency improvements, that could be reduced to as little as 3 exajoules. To put that into context, 3 exajoules is almost equivalent to all biofuels produced in 2019 and far surpasses the 0.005 exajoules of bio-based jet fuel produced in 2019. An exajoule is a measure of energy.
Flying less and improving airplanes’ energy efficiency, such as using more efficient “glide” landings that allow airlines to approach the airport with engines at near idle, can help reduce the amount of fuel needed. But even in our rosiest scenarios – where demand grows at 1% per year, compared to the historical average of 4% per year, and energy efficiency improves by 4% per year rather than 1% – aviation would still need about 3 exajoules of sustainable aviation fuels.
A rapid expansion in biofuel sustainable aviation fuels is easier said than done. It could require as much as 1.2 million square miles (300 million hectares) of dedicated land to grow corps to turn into fuel – roughly 19% of global cropland today.
Another challenge is cost. The global average price of fossil jet fuel is about about US$3 per gallon ($0.80 per liter), while the cost to produce bio-based jet fuels is often twice as much. The cheapest, HEFA, which uses fats, oils and greases, ranges in cost from $2.95 to $8.67 per gallon ($0.78 to $2.29 per liter), but it depends on the availability of waste oil.
Fischer-Tropsch biofuels, produced by a chemical reaction that converts carbon monoxide and hydrogen into liquid hydrocarbons, range from $3.79 to $8.71 per gallon ($1 to $2.30 per liter). And synthetic fuels are from $4.92 to $17.79 per gallon ($1.30 to $4.70 per liter).
Realistically, reaching net-zero emissions will likely also rely on carbon dioxide removal.
In a future with similar airline use as today, as much as 3.4 gigatons of carbon dioxide would have to be captured from the air and locked away – pumped underground, for example – for aviation to reach net-zero. That could cost trillions of dollars.
For these offsets to be effective, the carbon removal would also have to follow a robust eligibility criteria and be effectively permanent. This is not happening today in airline offsetting programs, where airlines are mostly buying cheap, nonpermanent offsets, such as those involving forest conservation and management projects.
Some caveats apply to our findings, which could increase the need for offsets even more.
Our assessment assumes sustainable aviation fuels to be net-zero carbon emissions. However, the feedstocks for these fuels currently have life-cycle emissions, including from fertilizer, farming and transportation. The American Society for Testing Materials also currently has a maximum blend limit: up to 50% sustainable fuels can be blended into conventional jet fuel for aviation in the U.S., though airlines have been testing 100% blends in Europe.
To meet the climate goals the world has set, emissions in all sectors must decrease – including aviation.
While reductions in demand would help reduce reliance on sustainable aviation fuels, it’s more likely that more and more people will fly in the future, as more people become wealthier. Efficiency improvements will help decrease the amount of energy needed to power aviation, but it won’t eliminate it.
Scaling up sustainable aviation fuel production could decrease its costs. Quotas, such as those introduced in the European Union’s “Fit for 55” plan, subsidies and tax credits, like those in the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act signed in 2022, and a carbon tax or other price on carbon, can all help achieve this.
Additionally, given the role that capturing carbon from the atmosphere will play in achieving net-zero emissions, a more robust accounting system is needed internationally to ensure that the offsets are compensating for aviation’s non-CO₂ impacts. If these hurdles are overcome, the aviation sector could achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.
This article is republished from The Conversation, an independent nonprofit news site dedicated to sharing ideas from academic experts. If you found it interesting, you could subscribe to our weekly newsletter.
Read more:
Electric planes are coming: Short-hop regional flights could be running on batteries in a few years
Bucking the trend: Is there a future for ultra long-haul flights in a net zero carbon world?
Candelaria Bergero's research was supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation and U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Steven J. Davis's research was supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation and U.S. Department of Agriculture.









Comments