Current News
/ArcaMax
News briefs
Trump-Biden debate launched 30 days of dizzying, rapid-fire events that changed history
DALLAS — There they stood. Two men perched at podiums in an audience-free television studio looking to win the first of two presidential debates. They couldn’t have had a clue how extraordinary the June 27 night would be. Neither did most Americans.
...Read more

'Once-in-a-lifetime caper': How did the US catch 'El Mayo,' the Sinaloa Cartel's top boss?
MEXICO CITY — Even among Mexican cartel bosses — a bunch known for lavish wealth, daring escapes and extreme brutality — Ismael “El Mayo” Zambada stood out.
He was a longtime partner of Joaquín “El Chapo” Guzmán, and together they built the Sinaloa Cartel into a global empire. Taking on an almost mythic status, he is rumored to...Read more

Fred Goldman files $117 million claim against O.J. Simpson's estate
LAS VEGAS — Fred Goldman, who won a civil judgment against former NFL star O.J. Simpson over the 1994 slaying of his son Ron Goldman, is seeking $177 million against Simpson’s estate in Las Vegas where the one-time running back died on April 10.
Goldman, represented by Reno attorney Michaelle Rafferty, on Wednesday filed and signed a ...Read more

South Korea accuses 3 Chinese students of illegally photographing San Diego-based carrier
South Korean authorities are reportedly investigating three Chinese students they say used a drone in late June to take images of the San Diego-based aircraft carrier USS Theodore Roosevelt while it was anchored in Busan harbor.
The alleged filming occurred June 23 and June 25 in an area where the students also had a view of South Korea’s ...Read more

Prince William removes Queen Camilla's sister from royal payroll after nearly 20 years
Prince William has removed Queen Camilla’s sister from the royal payroll after nearly two decades, according to the estate he inherited after King Charles was crowned the British monarch.
The 42-year-old Prince of Wales decided against rehiring Annabel Elliot as the estate’s interior designer, as noted in the Duchy of Cornwall’s most ...Read more

Lake Mead shoreline closes to overnight visitors after reports of crime, damage
LAS VEGAS — The National Park Service is closing a camping site in Lake Mead National Recreation Area after an influx of “residential-type visitors” led to damaged natural resources and high rates of crime, according to a release.
Starting Thursday, Government Wash will be closed to motor vehicle access and overnight camping. The roads ...Read more
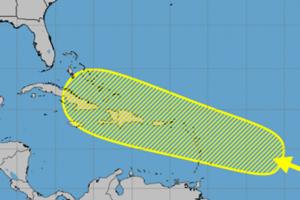
Disturbance in central Atlantic could develop near Caribbean islands
After a brief lull in storms forming in the Atlantic, forecasters are watching a disturbance nearing the eastern Caribbean Sea that could develop while it moves in a general direction over the Caribbean islands.
An “area of disturbed weather” over the central tropical Atlantic Ocean is forecast to interact with a tropical wave that is ...Read more

Luxury bags and a mini-fridge stuffed with cash: California schools embezzler is going to prison
LOS ANGELES — Jorge Armando Contreras seemed to enjoy a life beyond the means of a fiscal director for an Orange County school district.
He wore designer clothing, drove a BMW X5 and bought a new $1.5-million home in Yorba Linda, according to federal prosecutors.
He also had stacks of cash stuffed into Louis Vuitton purses and a mini-fridge...Read more

California's largest wildfire doubles in size, destroys scores of buildings, threatens historic resort
LOS ANGELES — The Park fire in Butte County — the largest blaze in California this year — exploded to more than 178,000 acres by Friday afternoon, with its rapid spread destroying scores of buildings and forcing more evacuations.
The growth of the fire over two days amid steady winds and high temperatures has been dramatic, with its ...Read more

Questions remain unanswered in case against former state lawmaker
In the ongoing criminal case against former Nevada Assemblyman Steven Brooks, prosecutors won’t say why they’ve dropped two of his charges and police have refused to release body camera footage of his arrest.
Brooks, 52, was arrested June 27 after a vehicle pursuit with police and faces charges of felony assault and disobeying a police ...Read more

Trump greets Netanyahu warmly at Mar-a-Lago after White House friction
Donald Trump gave Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu the warm welcome he was hoping for at Mar-a-Lago on Friday after the Israeli got a thinly veiled rebuke from presidential candidate Kamala Harris in Washington.
Trump greeted Netanyahu and his wife, Sara, at the top step of the gilded foyer at his Florida estate and criticized Harris’ ...Read more

Guard at 'rape club' prison faces new charges of sexually abusing inmates
LOS ANGELES — A new indictment accuses a former correctional officer at a now-shuttered federal women's prison in California dubbed the "rape club" of abusing more female inmates.
A federal grand jury issued a superseding indictment Thursday charging Darrell Wayne Smith with 15 counts of sexual abuse, including a civil rights violation, ...Read more

California's Park fire triples in size. More evacuated as blaze destroys at least 134 homes
SACRAMENTO, Calif. — The Park fire, raging in Butte and Tehama counties, continued to chew through the Northern California wilderness Friday, more than tripling in size since Wednesday night to just over 178,000 acres as more than 1,600 personnel battled flames amid tinder-dry and blistering conditions.
“The Park fire continues to burn very...Read more

Hiker from Arizona dies in 800-foot fall on southwest Colorado 14er
DENVER — A hiker from Arizona fell hundreds of feet to his death Wednesday while traversing a mountain ridge in southwestern Colorado, about 20 miles southwest of Telluride, according to sheriff’s officials.
The 21-year-old Arizona man, who has not been identified by name, was climbing a difficult section of the ridge between Mount Wilson ...Read more

3 charged with murder, arson and financial crimes in connection with death of Chicago firefighter
CHICAGO — Cook County prosecutors have charged three men with murder, arson and financial crimes in connection with the death of a Chicago firefighter last year while battling a blaze on the Far South Side.
Martez Cristler, 22, of Hammond, Indiana, and Nicholas Virgil, 37, of Riverdale, are charged with murder and arson. Anthony Moore, 47, of...Read more

Newsom calls on Oakland to allow more police chases, stop suspects from 'fleeing with impunity'
SACRAMENTO, Calif. — Gov. Gavin Newsom on Friday sent a letter to Oakland officials urging them to allow police to engage in more vehicle pursuits, contending that the limitations placed on officers contribute to public safety challenges in the city.
The California Highway Patrol inspired the governor's missive after the agency "observed ...Read more

2 women in custody battle shot dead near Gracie Mansion in apparent murder-suicide
NEW YORK — A 65-year-old retired probation officer from Chicago fatally shot her grandson’s mother on an Upper East Side street Friday just yards from Gracie Mansion, then turned the gun on herself, NYPD detectives said.
Kathleen Leigh shot Marisa Galloway, 45, on E. 88th St. near York Avenue at about 8:50 a.m., then killed herself in an ...Read more

Nebraska teen accused of causing train derailment for YouTube video
A Nebraska teenager has been accused of forcing a train to derail so he could record the incident and share it on YouTube, according to court records.
The 17-year-old, who was not named, was charged with two felony counts of criminal mischief in Lancaster County Juvenile Court, but prosecutors have already filed a motion to have the case ...Read more

Prince William removes Queen Camilla's sister from royal payroll after nearly 20 years
Prince William has removed Queen Camilla’s sister from the royal payroll after nearly two decades, according to the estate he inherited after King Charles was crowned the British monarch.
The 42-year-old Prince of Wales decided against rehiring Annabel Elliot as the estate’s interior designer, as noted in the Duchy of Cornwall’s most ...Read more
Father of California teen who was missing for a week is arrested
LOS ANGELES — The father of a Monterey Park teenager who disappeared for a week before being found safe outside a Glendale TV station on Tuesday was arrested Friday on suspicion of child abduction and other allegations, authorities announced.
Jeffrey Chao, the father of 15-year-old Alison Chao, was arrested on suspicion of child abduction, ...Read more
Popular Stories
- Kamala Harris is no Hubert Humphrey − how the presumed 2024 Democratic presidential nominee isn’t like the 1968 party candidate
- JD Vance’s selection as Trump’s running mate marks the end of Republican conservatism
- Harvey Weinstein hospitalized again with COVID-19 and double pneumonia
- Two of Mexico's top Sinaloa cartel leaders, including son of 'El Chapo,' arrested in El Paso
- Hospital-acquired infections are rising – here’s how to protect yourself in health care settings