What are nanoplastics? An engineer explains concerns about particles too small to see
Published in News & Features
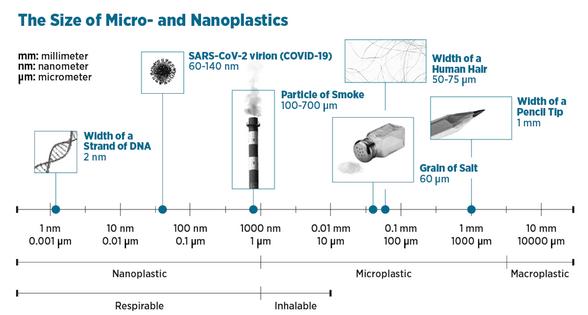
It’s become common to read that microplastics – little bits of plastic, smaller than a pencil eraser – are turning up everywhere and in everything, including the ocean, farmland, food and human bodies. Now a new term is gaining attention: nanoplastics. These particles are even tinier than microplastics – so small that they’re invisible to the naked eye.
Nanoplastics are a type of microplastic, distinguished by their extremely small size. Microplastics are usually less than 5 millimeters across; nanoplastics are between 1 and 1,000 nanometers across. For comparison, an average human hair is roughly 80,000-100,000 nanometers wide.
Nanoplastics are attracting growing concern thanks to recent technological advances that have made researchers more able to detect and analyze them. Their smaller size means that they are more easily transported over long distances and into more diverse environments than microplastics. They can more easily penetrate cells and tissues in living organisms, which could lead to different and more acute toxicological effects.
Studies in the past two years have found nanoplastics in human blood, in liver and lung cells, and in reproductive tissues such as the placenta and the testes. Around the world, nanoplastics have been found in the air, in seawater, in snow and in soil.
We already know that microplastics are present from the heights of Mount Everest to deep ocean trenches. Now there is growing evidence that nanoplastics are more prevalent than larger microplastics in the environment.
Nanoplastics are created when everyday products such as clothes, food and beverage packaging, home furnishings, plastic bags, toys and toiletries degrade. This can be caused by environmental factors such as sunlight or wear and tear from mechanical action. Many personal care products, such as scrubs and shampoos, can also release nanoplastics.
Like larger plastic particles, nanoplastics can come from a variety of polymer types, including polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride. Because plastic products are widely used, it is hard to avoid nanoplastics in our daily lives.
When plastics reach the nanoscale, they present unique questions and challenges because of their tiny size and varying surface properties and composition. Since nanoplastics are small, they can easily penetrate cells and tissues that larger particles cannot. If they accumulate within living organisms, they could potentially cause adverse biological effects.
The fate of nanoplastics in the environment is an ongoing research topic. Scientists don’t know yet whether nanoplastics further degrade in various environments into smaller particles, or into polymers, which are their basic building blocks – large molecules made of many small molecules strung together.
Finding nanoplastics is challenging because they are so tiny and have diverse chemical compositions and structures. Researchers are refining different approaches for detecting nanoplastics, using techniques including Raman spectroscopy, chromatography and mass spectrometry. These methods can see the shapes and analyze the properties of nanoplastic particles.
...continued











Comments